Understanding the Role of NAD and NMN
In the world of anti-aging and fitness supplementation, two names are quickly becoming headline stars: NAD and NMN. If you’ve heard of these molecules in podcasts, health blogs, or on supplement labels, you’re not alone. The “NAD vs NMN” debate is surging in popularity, with everyone from biohackers to aging researchers asking the same question: which is more effective for boosting cellular energy, longevity, and overall performance?
These two compounds play a key role in giving your body energy and helping it heal. Understanding the differences between the two and how they function can help you make an informed decision on which supplement may suit your goals best.
What Is NAD?
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a vital coenzyme found in every living cell. It plays a key role in energy metabolism, DNA repair, cellular signaling, and gene expression through the activation of proteins called sirtuins.
Forms of NAD: NAD⁺ and NADH
NAD exists in two main forms:
- NAD⁺ – the oxidized form, which accepts electrons
- NADH – the reduced form, which donates electrons
Together, they’re essential to converting nutrients into usable energy (ATP) inside your mitochondria.
Age-Related Decline in NAD⁺
Unfortunately, NAD⁺ levels decline with age, stress, and lifestyle factors. By the time you reach your 40s or 50s, your NAD⁺ levels could be nearly half of what they were in your youth, resulting in lower energy, slower metabolism, and reduced cellular repair capacity.
What Is NMN?
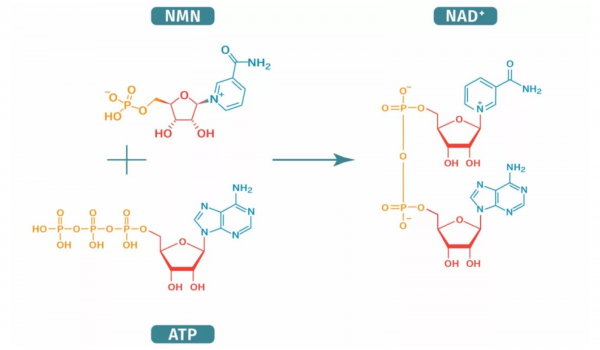
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) helps your body make NAD⁺ directly. In simple terms, it’s one of the key building blocks your body uses to naturally produce more NAD⁺.
The NAD⁺ Salvage Pathway
NMN plays a critical role in what scientists call the “salvage pathway”—your body’s way of recycling NAD⁺. Supplementing with NMN may support NAD⁺ regeneration more efficiently than supplementing with NAD⁺ directly.
Natural Sources of NMN
You can find NMN in small amounts in foods like:
- Broccoli
- Avocados
- Edamame
- Cabbage
However, dietary intake alone doesn’t offer therapeutic levels—this is where NMN supplements come into play, often delivered in capsule, powder, or sublingual forms.
NAD vs NMN: Main Differences
Molecular Structure & Absorption
- NMN is a smaller molecule that can be easily absorbed and transported into cells.
- NAD⁺ is larger and less bioavailable when taken orally. In most cases, the body breaks it down into precursors like NMN before it can be utilized.
This makes NMN a more practical option for oral supplementation when your goal is to raise intracellular NAD⁺ levels.
Bioavailability & Efficiency
Studies suggest that NMN is more effective at raising NAD⁺ levels inside cells when taken orally.
- NAD⁺ IV infusions can increase NAD⁺ quickly in the bloodstream, but may not raise cellular NAD⁺ as efficiently due to limited transport across cell membranes.
Delivery Methods
NMN Supplements:
- Capsules
- Sublingual tablets
- Powders
NAD⁺ Supplements:
- Oral capsules (less effective)
- IV infusions (popular in wellness clinics)
- Nasal sprays
Biohackers often turn to NAD⁺ IV drips for fast recovery or mental clarity, but these are costly and less practical for daily use.
Health Benefits Compared

Energy & Metabolism
Both NAD and NMN support ATP production, your cells’ primary energy currency. For fitness enthusiasts, this means more sustained energy during workouts and quicker recovery afterward.
DNA Repair & Longevity
NAD⁺ is required by enzymes like sirtuins and PARPs, which:
- Repair damaged DNA
- Regulate inflammation
- Extend cellular lifespan
Higher NAD⁺ levels have been linked to slower biological aging and improved mitochondrial function.
Inflammation & Cardiovascular Health
NMN has shown promise in reducing inflammatory markers like IL‑6 and improving arterial flexibility, especially in older adults. This can translate into better heart health and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Cognitive Function
- NAD may support mental clarity, neurotransmitter balance, and brain cell health.
- NMN supplementation has been studied for age-related cognitive decline, with promising results in memory and focus retention.
Safety & Side Effects
NMN
- Generally considered safe up to 500–900 mg/day
- Mild side effects: Gastrointestinal discomfort, flushing
- Clinical studies have shown few adverse effects in short-to-mid-term usage
NAD
- IV therapy may cause nausea, cramping, or light-headedness in some users
- Long-term safety of oral NAD⁺ supplementation is still under investigation
- Using this without a doctor’s supervision can be risky, especially for those with existing health concerns.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting new supplements—especially if you’re managing a medical condition or taking other medications.
Dosage & Practical Use
NMN
- Dosage Range: 100 to 900 mg/day
- Best taken in the morning to align with circadian NAD⁺ production
- Combine with exercise and a clean diet for optimal effects
NAD
- Oral Dosage: ~200–300 mg/day
- IV Doses: Vary widely, often administered in a clinical setting
- Best used for short-term boosts (e.g., recovery, cognitive reset)
For consistent cellular support and anti-aging benefits, NMN is more user-friendly and cost-effective. Consider cycling supplements (e.g., 5 days on, 2 days off) to maximize benefit and minimize tolerance build-up.
Relevant art: NMN Supplement Benefits, Side Effects, and Dosage
Which One Should You Choose?
Goal-Based Recommendations
- Low energy or fatigue?
→ Try NMN for steady NAD⁺ support and mitochondrial health.
- Need a cognitive boost or recovery after intense workouts?
→ NAD⁺ IV therapy might provide fast relief.
Convenience & Lifestyle Fit
- NMN is ideal for daily use at home.
- NAD⁺ often requires visits to clinics and is more expensive.
Budget & Accessibility
- NMN supplements are more widely available, cost-effective, and easy to dose.
- NAD⁺ therapies may be pricey, and not all products are created equal—look for purity testing and clinical-grade standards.
Final Tip
For optimal results, combine NAD or NMN supplementation with:
- Daily exercise
- Intermittent fasting
- Antioxidant-rich diet (think leafy greens, berries, and nuts)
FAQs
Can I take NAD and NMN supplements together?
Yes, many users take them together. NMN helps boost NAD⁺ production, and NAD⁺ may offer fast-acting benefits. Try a lower dose first to check how it affects you.
How long does it take to feel the effects of NMN or NAD?
Some users notice better focus and energy levels in as little as 1 to 2 weeks. For anti-aging or cellular benefits, consistency over months is key.
Are NAD and NMN supplements safe for long-term use?
Short-term studies are promising. However, long-term human trials are ongoing. Stick to clinically tested brands and seek medical advice.
Is NAD better than NMN for anti-aging benefits?
NMN may be more effective in sustained NAD⁺ elevation, making it a better long-term anti-aging strategy for most people.
Conclusion
When it comes to NAD vs NMN, both compounds play crucial roles in supporting cellular health, energy, and longevity. However, NMN often has the upper hand in terms of oral bioavailability, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness.
- Choose NMN for steady energy, anti-aging, and cellular repair.
- Use NAD⁺ infusions for short-term mental clarity or performance recovery.
Whichever you choose, always prioritize high-quality supplements, get professional guidance, and support your health journey with a balanced lifestyle.

Ready to support your cellular health?
You can buy our premium-grade NMN and NAD⁺ supplements at AneraLife.
Our products are backed by science, purity-tested, and trusted by fitness enthusiasts and wellness professionals alike.
Visit aneralife.com to shop now and take the next step in your longevity and performance journey.